______
/ | ________
/ |____ / \
/ | \/ _ \
\ ___ /_\ \
\ \_/ . \
\ /\_____/ /
\________/ | /
|______/
[THE_EXPR_METHOD] 007 Modulus Djent
The modulo operator can be useful in making (pseudo) generative patterns. Not only its relatively easy to use, the process is also responsive to parameter changes. In other words, complex structures can be derived from simple operations, the transitions between perceivingly different patterns can also be quickly made.
The following two examples illustrates a simple usage of modulo and the resulting patterns:
if($v1%4 == 0, 1, 0): COUNTER: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F . . . . PATTERN: 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 . . . . if($v1%5 == 0, 1, 0): COUNTER: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F . . . . PATTERN: 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 . . . .
Such implementation don’t produce interesting results by itself, unless the patterns are stacked/layered against each other.
However, by chaining modulo operators one after another, the result quickly becomes more complex. For example:
if(($v1%5)%3 == 0, 1, 0): COUNTER: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F . . . . PATTERN: 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 . . . . if((($v1%7)%4)%3 == 0, 1, 0): COUNTER: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F . . . . PATTERN: 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 . . . . if((($v1%11)%7)%4 == 0, 1, 0): COUNTER: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F . . . . PATTERN: 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 . . . .
The general principle is thus to use progressively smaller values after each modulo operator, so to nest smaller counts inside of larger loops. Often, these divisors, especially towards smaller ones, can be modulated by other time measure, so to increase the diversity of the resulting pattern.
Furthermore, since largest divisor determines the length of the entire pattern, by modulating it would also produce different pattern, even if the rest of the expression remains the same. Consider the following:
if(($v1%5)%3 == 0, 1, 0) vs. if(($v1%7)%3 == 0, 1, 0): COUNTER: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F . . . . PATTERN: 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 . . . . PATTERN: 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 . . . .
Notice that the examples so far uniformly select the first count to give the final structure, but the following can also be considered:
if(($v1%5)%3 == $v2) where $v2 is a modulated signal to select which element in the count is to be used.
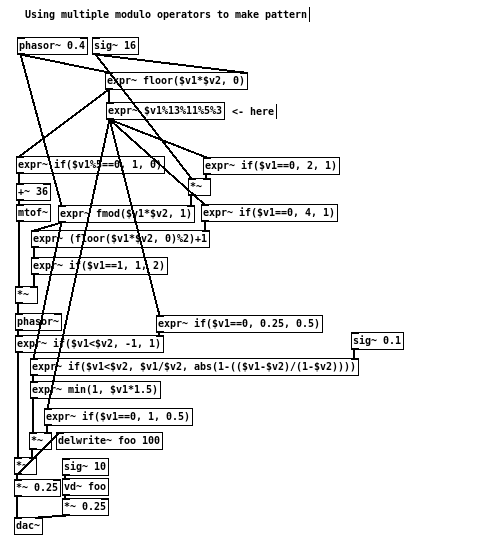
Here is an quick example using modulo operator to make Djent:)
Exercise:
- What other ways can modulo be useful to make/manipulate patterns?
- How to use phase shift to further process the resulting pattern?
Leave a Reply